NFT
Why Are NFTs Bad? The Problem And Legal Issues

Why Are NFTs Bad? This pressing question underscores today’s heated discussions around Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). Despite the buzz, many investors are left grappling with unsellable NFTs, questioning their value and security. This article cuts through the noise to examine the critical issues and legal challenges surrounding NFTs.
We navigate the complex NFT laws, dissect the reasons behind the unsellable nature of some digital assets, and address the underlying problems fueling the skepticism. With focused insights, we aim to shed light on the darker aspects of NFTs to answer the question: are NFTs bad?
Why Are NFTs Bad?
The question “Why are NFTs bad?” resonates in the digital world, particularly among those cautious about the rapidly evolving blockchain technology. NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, have garnered attention for their unique ability to represent ownership of digital assets. However, beneath the surface of this innovative technology lies a web of concerns that have led many to question their overall value and impact.
Understanding NFTs: A Brief Overview
NFTs are digital tokens that represent ownership of unique items, using blockchain technology to certify authenticity and ownership. Each NFT stands out as distinct, unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are fungible and allow for one-to-one exchanges. They can represent anything digital, such as art, music, or even tweets.
NFTs derive their uniqueness from granting a feeling of exclusivity and ownership over digital assets, which have traditionally been easily replicated and distributed. By tokenizing these assets on a blockchain, NFTs create a digital scarcity and a verifiable way to claim ownership.
However, the rise of NFTs has not been without controversy. Their detractors point to several key issues: technical issues questioning the longevity of NFTs, the potential for market manipulation, and the creation of a speculative bubble where the value of digital assets is highly uncertain. Furthermore, the legal landscape surrounding NFTs is still evolving, with questions about copyright and ownership rights at the forefront.
Exploring The Main Question: Why Are NFTs Bad?
While NFTs have their benefits, the growing concerns cannot be overlooked. The main question, “Why are NFTs bad?” stems from several critical issues associated with their use and functionality.

Technical Challenges And Longevity Concerns
The appeal of NFTs on blockchains such as Ethereum is diminished by various technical challenges, raising questions about their long-term viability and dependability as digital assets. Here are some technical reasons for “why are NFTs bad”:
- Off-Blockchain Asset Storage: Most NFTs, especially on Ethereum, link to digital assets like images stored off the blockchain due to Ethereum’s size and cost constraints. These assets are often hosted on platforms like IPFS (InterPlanetary File System), not directly on the blockchain.
- External URL Vulnerability: The use of external storage like IPFS raises questions about the longevity and accessibility of the linked digital assets. The potential obsolescence of these platforms poses a risk to the permanence of NFTs.
- Blockchain-Specific Uniqueness: The uniqueness of an NFT is limited to its native blockchain, like Ethereum. The same asset can be tokenized on different blockchains, challenging the notion of uniqueness.
- Duplicate NFT References: NFTs can reference the same digital asset via HTTP links, leading to multiple NFTs for a single asset within the same blockchain, contrary to their non-fungible nature.
Market Manipulation And Speculative Bubble
The NFT market is not just a platform for digital creativity but also a hotbed for speculation and potential market manipulation, raising significant concerns. Following are some market-related reasons for “why are NFTs bad”:
- Speculative Investments: NFTs have become symbols of speculative investment, with prices often driven by hype rather than intrinsic value. High-profile sales, like that of Beeple’s artwork, have attracted a wave of investors looking to capitalize on potential market booms. This speculation can inflate prices artificially, creating a bubble where the value of NFTs is grossly overestimated.
- Risk Of Market Manipulation: The NFT marketplace is vulnerable to manipulation due to its relatively unregulated nature and the opacity of transactions. There have been instances where artists or sellers artificially inflate the value of an NFT by purchasing their own assets through third parties. This tactic creates a false impression of high demand and value, luring unsuspecting buyers into overpaying.
- Impact Of Celebrity Endorsements: The involvement of celebrities and influencers in promoting NFTs further fuels the speculative bubble. Their endorsements can lead to rapid spikes in prices and interest, often without a sustainable basis. While celebrity involvement has brought mainstream attention to NFTs, it also raises questions about the genuine value and long-term viability of these assets.
- Volatility And Unsustainability: High volatility marks the NFT market, featuring significant fluctuations in value. This instability renders NFT investments risky, especially for individuals not deeply familiar with the digital asset landscape.
Legal Ambiguity
The burgeoning world of NFTs is mired in legal ambiguities, making it a complex landscape to navigate for creators, collectors, and investors alike. Below are some legal reasons for “why are NFTs bad”:
Unclear Copyright And Ownership Rights:
One of the fundamental legal challenges with NFTs is the ambiguity surrounding copyright and ownership rights. Purchasing an NFT often grants the buyer ownership of a unique token, but not necessarily the copyright of the underlying digital asset. This distinction can lead to confusion and disputes over what buyers are actually entitled to when they acquire an NFT.
Varying International Laws:
The legal recognition of NFTs varies significantly across different jurisdictions. While some countries may have specific regulations governing digital assets, others lack clear guidelines. This inconsistency presents challenges, particularly in cases involving cross-border transactions or disputes.
Smart Contract Complexities:
NFTs operate on smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. However, the legal status of these contracts is not always clear. Issues arise when smart contracts, which are immutable once deployed, contain errors or do not align with legal standards. Rectifying these issues can be complicated and may require litigation.
Regulatory Uncertainty:
The regulatory landscape for NFTs is still in its infancy. Financial regulators in various countries are grappling with how to classify NFTs—whether as securities, commodities, or a completely new asset class. This lack of regulatory clarity adds to the uncertainty, particularly regarding compliance with existing financial laws and anti-money laundering (AML) requirements.
Liability And Consumer Protection:
The decentralized nature of NFT marketplaces often leaves consumers with limited recourse in cases of fraud, theft, or disputes. In such scenarios, the issue of liability remains mostly unresolved, and consumer protection mechanisms are not as strong as those in traditional financial markets.
NFT Pros And Cons
The world of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) presents a mixed bag of advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these pros and cons is essential for anyone looking to engage with NFTs, whether as creators, collectors, or investors.
Pros Of NFTs:
- Digital Ownership And Provenance: NFTs provide a clear proof of ownership and provenance for digital assets. They enable artists and creators to monetize digital works, which were previously easy to replicate and difficult to sell as unique pieces.
- Market Expansion For Artists: NFTs have opened up new markets for digital artists and creators, allowing them to reach a global audience. This democratization of art sales has empowered artists, especially those outside the traditional gallery system.
- Innovation And Creativity: The NFT space encourages innovation and creativity, particularly in digital art and multimedia. It has sparked new forms of artistic expression and collaboration.
- Collectibility And Investment: For collectors, NFTs offer a new avenue for investment in digital art and collectibles. The unique nature of NFTs makes them appealing as collectible items.
Cons Of NFTs:
- Technical Issues: On blockchains like Ethereum, NFTs present several technical issues, questioning their longevity. Being aware of these issues is crucial.
- Market Volatility And Speculation: The NFT market is highly volatile, with values fluctuating dramatically. This instability, coupled with speculative investments, poses risks for buyers and sellers.
- Intellectual Property Issues: The legal ambiguity around copyright and ownership rights in NFTs creates complications for intellectual property law. Buyers might not fully understand what rights they are acquiring, leading to potential legal disputes.
- Accessibility And Inclusivity Issues: Despite their potential for democratizing art, NFTs also pose challenges in terms of accessibility and inclusivity. The technical and financial barriers to entry can be high, limiting participation to a more tech-savvy and financially capable audience.
The Dark Side: Unsellable NFTs And Market Risks
The world of NFTs is not just about innovation and lucrative opportunities. There’s a darker side to this market, characterized by the phenomenon of unsellable NFTs and significant market risks that raise critical questions about the overall safety and soundness of investing in these digital assets. This adds another layer to the question “why are NFTs bad.”
The Reality Of Unsellable NFTs
While NFTs have been sold for staggering amounts, the reality is that not all NFTs find buyers, leading to a growing concern over unsellable NFTs. Several factors contribute to this situation:
- Market Saturation: As more creators and investors flood into the NFT space, the market is becoming increasingly saturated. This saturation makes it harder for individual NFTs to stand out, reducing their likelihood of being sold.
- Speculative Nature: Many NFTs are bought for speculative purposes, with the hope of reselling for a profit. When the speculation bubble bursts, or if the hype dies down, the value of these NFTs can plummet, making them difficult to sell.
- Lack Of Intrinsic Value: Some NFTs may lack intrinsic artistic or collectible value, being created solely for the purpose of capitalizing on the trend. These NFTs may struggle to find a market.
- Liquidity Issues: The NFT market is not as liquid as other investment markets. Selling an NFT, especially at a desired price point, can be challenging and time-consuming.
Platforms like Unsellable specialize in purchasing these low-value NFTs for tax write-off purposes.
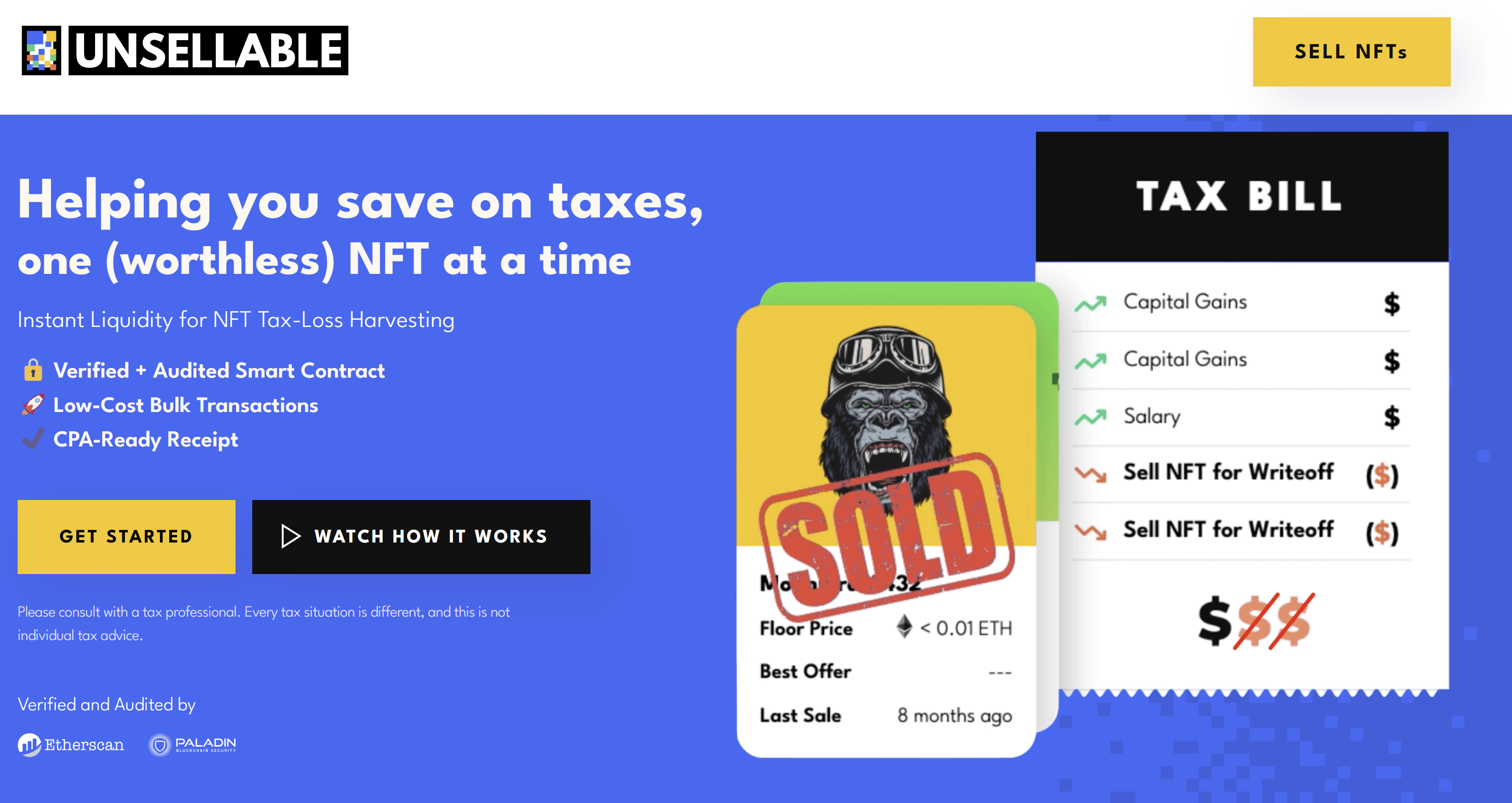
Are NFTs Bad?
The question “Are NFTs bad?” is complex. NFTs themselves are a neutral technology with potential for positive use, such as supporting artists and creating unique digital experiences. However, the issues of market saturation, speculative bubbles, and technical concerns add a negative aspect to this technology. The answer largely depends on how NFTs are used and the awareness of the buyers and sellers about the risks involved.
Are NFTs Safe?
The safety of investing in NFTs is a matter of perspective and depends on various factors:
- Technical Issues: NFTs on Ethereum face several problems that investors should be aware of.
- Market Volatility: The high volatility of the NFT market can lead to significant financial risks for investors.
- Legal and Technical Risks: As discussed earlier, there are legal ambiguities and technical challenges associated with NFTs, which can impact their long-term viability.
- Scams And Fraud: The NFT space, like any emerging market, is susceptible to NFT scams and fraudulent activities, which can pose risks to less experienced investors.

NFT Laws: Legal Challenges
Navigating the complex legal landscape of NFTs poses a challenge, given that these digital assets intersect various aspects of law in ways that are still evolving and being defined. The dynamic and rapidly evolving nature of NFTs has left lawmakers and stakeholders working to catch up with the legal implications which adds another argument to the question “why are NFTs bad”.
NFT Laws Decoded
The application of existing laws to NFTs is a challenging task, primarily because NFTs are a novel concept that doesn’t fit neatly into traditional legal categories. Intellectual property rights are at the forefront of legal concerns. When someone purchases an NFT, they acquire a token that represents ownership, but the extent of this ownership is often misunderstood. It rarely includes the right to reproduce or distribute the underlying digital asset, leading to potential legal disputes over copyright infringement and ownership rights.
Consumer protection laws are also critical in the NFT marketplace. These laws are designed to protect buyers from deceptive practices. However, the decentralized and often anonymous nature of blockchain transactions makes the enforcement of such laws challenging. The risk of fraud and misrepresentation is high, and buyers may find themselves with limited recourse in cases of dispute.
The classification of NFTs under financial regulations is another area of legal ambiguity. The structure and nature of certain NFTs might classify them as securities. For example, the US Securities and Exchange Commission charged Stoner Cats 2 for conducting an “unregistered offering of crypto asset securities,” depending on their specific characteristics. This categorization subjects them to stringent regulatory requirements, including registration and disclosure obligations under securities laws. However, the lack of clear guidance from regulatory bodies creates uncertainty for NFT issuers and investors.
NFT Legal Issues: A Detailed Analysis
Legal issues in the NFT space are diverse and multifaceted. Copyright and ownership disputes are common, particularly as the lines between digital ownership and copyright ownership are blurred. These disputes often involve multiple parties, including artists, digital platforms, and collectors, each with differing interpretations of their legal rights.
Smart contracts, which are the backbone of NFT transactions, present their own set of legal challenges. While these contracts are designed to be self-executing and immutable, they are not immune to legal scrutiny. Disputes can arise when the terms encoded in smart contracts conflict with statutory laws or when there are errors in the code. The resolution of such disputes often requires litigation, which can be complex and costly.
Taxation of NFT transactions is an emerging area of legal concern. The tax implications for buying, selling, or creating NFTs are not straightforward, and tax authorities are still determining how to apply existing tax laws to these transactions. This uncertainty complicates financial planning for participants in the NFT market and raises the risk of unintended tax liabilities.
The Evolving Landscape Of NFT Legality
As the NFT market continues to grow, so does the legal framework that surrounds it. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are beginning to recognize the need for specific regulations that address the unique aspects of NFTs. These emerging regulations aim to provide clarity and stability to the market, but they also bring new compliance challenges.
The global nature of NFT transactions adds another layer of complexity. NFTs are often bought and sold across international borders, bringing into play different legal jurisdictions and regulatory standards. Harmonizing these diverse legal systems is a daunting task and one that is critical for the development of a cohesive global NFT marketplace.
Legal cases involving NFTs are increasingly making their way through courts, setting important precedents that will influence future legal interpretations and regulations. These cases cover a range of issues, from copyright disputes to the enforceability of smart contracts, and their outcomes will have significant implications for the NFT industry.
In conclusion, the legal challenges surrounding NFTs are as dynamic and multifaceted as the technology itself. From intellectual property concerns to regulatory compliance, the legal aspects of NFTs require careful navigation. As the market evolves, so too will the laws and regulations that govern it, shaping the future of this innovative digital asset class.
The Problem With NFTs
The world of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) is marked not only by innovation and opportunity but also by significant problems that raise concerns and contribute to the question, “Why are NFTs bad?”.
Analyzing More Of The Problem With NFTs
A closer look reveals several underlying problems with NFTs:
- Perceived Value Vs. Real Value: A core problem with NFTs is the disconnect between their perceived and real value. The worth of many NFTs is often driven by hype and speculation rather than tangible artistic or utilitarian value. This discrepancy can lead to a volatile market where prices do not reflect the true value of the underlying digital asset.
- Cultural And Ethical Concerns: The NFT craze has raised cultural and ethical questions. It challenges traditional notions of art ownership and creation, potentially commodifying artistic expression in unprecedented ways.
- Impact On Artistic Integrity: For artists, the lure of NFTs can sometimes lead to a compromise in artistic integrity. The pressure to create content that is more likely to sell in the NFT market can influence artistic decisions, potentially leading to a homogenization of digital art.
- Accessibility And Digital Divide: The NFT ecosystem tends to favor those with access to specific technological resources and knowledge. This digital divide excludes a large segment of potential creators and collectors, particularly those from underprivileged backgrounds or regions with limited access to advanced technology.
Blockchain Legal Issues
Earlier discussions have addressed the legal challenges of blockchain, the underlying technology of NFTs, but further exploration reveals additional nuances worth considering:
- Data Privacy Concerns: Blockchain’s transparency and immutability, while strengths, also raise data privacy concerns. Once on the blockchain, information becomes almost impossible to remove, potentially leading to privacy issues, especially with personal data involved.
- Smart Contract Liabilities: Smart contracts are prone to coding errors or unforeseen legal implications. These liabilities can lead to complex legal scenarios where the responsibilities and liabilities of parties in a blockchain transaction are unclear or disputed.
- Cross-Border Enforcement: Enforcing legal decisions across borders is a significant challenge in blockchain transactions. When a dispute arises, the international and decentralized nature of blockchain makes it difficult to enforce judgments or legal actions.
- Emerging Legal Frameworks: As governments and regulatory bodies start to catch up with blockchain technology, new legal frameworks are emerging. These frameworks aim to address the unique challenges posed by blockchain but also create a shifting legal landscape that can be difficult for participants to navigate.
In conclusion, the problems with NFTs extend beyond simple technical or market issues, encompassing broader cultural, ethical, and legal challenges. As the NFT space matures, addressing these multifaceted problems will be crucial for its sustainable and responsible growth.
FAQ: Why Are NFTs Bad?
This FAQ section aims to succinctly address some key questions surrounding NFTs, especially everything about the questions “why are NFTs bad?”
Why Are NFTs Bad?
Critics often target NFTs for their environmental impact, market volatility, and legal uncertainties. Concerns also include the potential for exacerbating the digital divide. The perspective on whether NFTs are “bad” varies based on individual viewpoints and contexts.
NFT Laws: What Investors Should Know?
Investors should note that the legal framework around NFTs is evolving. Key considerations include copyright and financial regulations, as well as the market’s inherent volatility and potential legal risks.
Are NFTs Unsellable?
Not all NFTs are unsellable, but market saturation and fluctuating values can affect their salability. The speculative nature of the market adds to the uncertainty regarding the sale and value of NFTs.
Are NFTs Bad?
Whether NFTs are “bad” is subjective. While they offer innovative digital asset ownership, their environmental costs, potential for market manipulation, and legal challenges are significant drawbacks.
What Is The Problem With NFTs?
The main issues with NFTs include environmental concerns, market instability, accessibility challenges, and legal ambiguities, highlighting the need for sustainable practices and clear regulations.
What’s The Problem With NFTs?
NFTs face environmental, economic, legal, and ethical challenges, including energy consumption, market fluctuation, and impacts on artistic and cultural values.
Are NFTs Legal?
NFTs are legal, but they operate in a complex regulatory landscape that varies across regions. The legality involves considerations around transactional frameworks and compliance with existing laws.
Featured image from Shutterstock
NFT
Pudgy Penguins Linked Abstract Chain Goes Live On Mainnet

In an astounding development, Abstract Chain, an Ethereum Layer-2 network launched by Pudgy Penguins’ parent company, Igloo Inc., has gone live on the mainnet. Reportedly, the Ethereum-based Layer 2 blockchain is designed to empower crypto communities and facilitate user-centric Web3 applications.
Despite Abstract Chain’s mainnet launch, Pudgy Penguins’ PENGU token has seen a massive decline. While the token’s descent aligns with the broader market trend, the community remains anxious about its further movements.
Igloo’s Abstract Chain Sees Mainnet Launch
Abstract Chain is now live on the mainnet, opening it up to the public for usage. According to a press release, Abstract Chain is now available for consumers, with the mission of driving mass crypto adoption. Developed by Igloo Inc., the parent company of the popular NFT collection, Pudgy Penguins, Abstract Chain focuses on providing a user-friendly experience.
On January 26, Pudgy Penguins CEO Luca Netz shared an X post announcing Abstract Chain’s mainnet launch. Netz proclaimed that the launch would take place on January 27, effective today.
MONDAY MAINNET ✳️🐧 https://t.co/Cp5naJdoB4
— Luca Netz 🐧✳️ (@LucaNetz) January 25, 2025
Commenting on the launch of Abstract, Netz stated,
The launch of Abstract is more than just a technical milestone—it’s a shift in how everyday users – and not just crypto natives – experience blockchain. We’ve built Abstract to strip away the complexities of crypto, offering an intuitive and enjoyable experience that empowers users to explore and create effortlessly.
Igloo Introduces the Consumer Blockchain Platform- The Portal
Meanwhile, the Abstract Blockchain unveiled The Portal, which the L2 network describes as the consumer blockchain platform. In a more intriguing description, the blockchain network calls The Portal a “Digital Theme Park of Fun” that revolutionizes the way billions interact with blockchain technology.
The Portal allows users to set up a wallet using just their email address, providing seamless access to a vast ecosystem featuring over 100 community-driven decentralized applications (dApps). The platform aligns with Abstract’s vision of merging the simplicity of Web2 with the transformative potential of Web3.
Abstract Chain’s Zero-Knowledge Rollups
Leveraging ZKsync’s ZK stack, Abstract Chain utilizes zero-knowledge rollups. Reportedly, it provides scalable and cost-effective on-chain solutions with reduced transaction fees.
In response to Abstract’s mainnet launch, ZKsync co-founder Alex Gluchowski cited,
For blockchain to reach the masses, we must abstract away the complexity. Users need to experience better apps, builders need to have more engaged users, and creators need to be rewarded for their efforts – while cutting out unnecessary middlemen. Abstract building for everyone, not just Web3 power-users, is the path to get the next billion onchain.
Pudgy Penguins’ PENGU Token Falls 11%
Echoing the broader market sentiment, Pudgy Penguins’ PENGU token dropped by more than 11% in a day despite Abstract Chain’s mainnet launch. Mainly triggered by China’s DeepSeek AI launch, the crypto market is bleeding today, with Bitcoin slipping below $99k.
As of press time, PENGU is exchanging hands at $0.2282, with a decrease of 4.5% over the last seven days. In a month, the token has seen a massive fall of 37%. However, PENGU’s 24-hour trading volume has seen a hike of 48%, currently at $376 million. PENGU token’s substantial decline follows its last month’s remarkable surge that earned a staggering 14,500x return for an investor. With an initial investment of just $6, the investor made a profit of $87K.
Disclaimer: The presented content may include the personal opinion of the author and is subject to market condition. Do your market research before investing in cryptocurrencies. The author or the publication does not hold any responsibility for your personal financial loss.
NFT
CyberKongz Receives Wells Notice from SEC, Vows to Fight for NFT Clarity

The NFT collection CyberKongz said the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) will likely charge it.
In a post on X on Monday, the collection said it received a Wells Notice, a letter from the SEC staff that recommends an enforcement action. It commented that the SEC is trying to pull through its laws before Joe Biden’s administration is over.
CyberKongz: “We Will Not Be Silenced”
In a statement, the NFT collection said it was disappointed with the approach of the SEC and vowed to stand up for and fight for greater clarity in the NFT space.
It also mentioned that the SEC raised concerns about its business with Genesis Kongz in April 2021, describing it as a “contract migration.”
It said:
CyberKongz added it intends to fight for clearer crypto regulation, particularly regarding NFT projects.
Eyeing Trump’s Crypto-Friendly Stance
The NFT collection has been vocal about the current administration, which it claims is anti-crypto in its approach. Just recently, as the US Senate Banking Committee was preparing to vote on SEC Commissioner Caroline Crenshaw’s renomination, lawyer Bill Hughes raised concerns about her stance on cryptocurrency regulation. Hughes argued that her renomination one could see as politically hostile to the crypto industry. This stands in contrast to the increasing support for crypto-friendly policies under the incoming administration.
CyberKongz is optimistic that the new administration will provide a more level playing field with a more just regulatory framework. In the meantime, the team comited to support all NFT projects on every blockchain platform.
In the past year, the SEC has acted against several cases related to NFTs. This includes lawsuits against podcast studio Impact Theory and Stoner Cats 2 LLC over unregistered NFT offerings that raised millions. The commission also doled out a Wells Notice to NFT marketplace OpenSea, signaling potential enforcement action.
It is up to wait and see how this enforcement will unfold in the transition of the commission’s leadership. The current SEC Chairman Gary Gensler announced his departure on January 20, in concert with the inauguration of President-elect Donald Trump. Trump has named former SEC Commissioner Paul Atkins, considered friendlier to the crypto industry, as the head of the SEC.
Disclaimer: The presented content may include the personal opinion of the author and is subject to market condition. Do your market research before investing in cryptocurrencies. The author or the publication does not hold any responsibility for your personal financial loss.
NFT
Unyted + Vesa

Unyted we (meta) stand
Many of the fancy metaverse projects take loooong to build and often require developers and budgets just to stay alive. In fact, one of my favorite ones had the whole company collapse around it in the build phase. I absolutely love what we’ve built with Superworld, for example, and what we’re about to release with Asvoria. Both of these require heavy machinery and rotation to come to life—and to be maintained.
Enter Unyted and my newest spatial Web3 space, which allows me to deliver fluent, up-to-date presentations on what’s happening now while also providing an overview of my entire career. I built it mostly by myself, with some guidance and glitch-fixing help from the team—special thanks to Tijana, Saskia, and Florian. I can update it in minutes to include a new project, presentation, or missing link. It’s freeing and necessary.
Unyted is at the forefront of spatial computing, offering innovative solutions that empower users to create, own, and monetize immersive 3D virtual environments. Their platform is designed to facilitate seamless transitions into the metaverse, providing tools for education, collaboration, and personalized digital experiences.
Link to join the metaverse
Link to join the X spaces.
Join us for a session with Ador, Bitcoin LIVE and others tomorrow 20.00 CET
Starting Thursday, we’ll kick things off with a joint presentation with Ador, and from there, we’ll host regular spaces that people can join visually. X is great for connecting with people, but for an artist, a lot is still missing from the full experience. Let’s see if we can bring these two innovations together in a sensible way.
 Watch the Tijana introduction to Unyted as well as my keynote held some time ago regarding web3, metaverse and creativity.
Watch the Tijana introduction to Unyted as well as my keynote held some time ago regarding web3, metaverse and creativity.
Delivering the Metaverse
They’re just starting out, and sure, sure there are a few glitches, but I’ve already given a couple of presentations that feel like a real departure from the world of Zoom. Nothing is ever perfect and getting going and constantly working on it is what keeps the thing alive.
It’s a step closer to delivering something of real value in the metaverse. People showed up to my first keynote in the space done together, they asked questions and then some were left to wonder around the space to explore it on their own. Promises kept. Those matter, after the last run.

I’ve been friends with Florian Krueger since the early blockchain days in London back in 2018, and we’ve collaborated on several projects. He remains one of my favorite people in the crypto space—always looking out for his people and tirelessly fighting for the ethical side of it. I was happy to hear he was starting a new venture and that I could also be a part of.
If you prefer the (virtual) city life?
Key Features of Unyted:
- Modular Environments: Unyted enables users to design and customize digital spaces, such as virtual homes, offices, or campuses, reflecting their unique vision. These environments can be monetized, allowing creators to generate revenue through their virtual properties.
- EdTech Solutions: The platform offers immersive educational experiences with features like AI-driven personalized learning paths, customizable avatars, and virtual classrooms. These tools aim to enhance student engagement and retention, providing scalable and cost-effective solutions for educational institutions.
- Data Protection and Security: Operating under EU regulations and compliant with GDPR, Unyted ensures top-tier data protection. Users maintain complete control over their personal and institutional data, upholding responsible practices in the metaverse.
- Sustainability Commitment: Unyted is dedicated to sustainability, calculating energy consumption and offsetting carbon emissions for each project. Through Unyted.World, users can stake tokens specifically for carbon offsetting, promoting environmental responsibility within the digital landscape.
In many ways what is important about the metaverse is our ability to pre-visualise the world we would like to live in, and then walk toward that direction.
Founded in 2022 by Gaby K. Slezák and Florian Krueger, Unyted envisions a decentralized, independent metaverse where users have equal access to a secure three-dimensional internet. Their mission is to empower individuals to shape their digital futures, fostering a community where creativity and collaboration thrive.
For those seeking to explore the metaverse, Unyted offers consulting services to guide organizations through VR, AR, blockchain, Web3, and Web4 technologies. Their seasoned team provides strategy insights and design expertise to craft unique digital experiences aligned with organizational visions.
Unyted stands as a visionary force in the evolving digital landscape, pioneering innovation while prioritizing user ownership, open collaboration, data protection, and sustainability.
Ador aka BitSavage will join us for the Monday talk in which we also dwell deeper into DAF – the Department of Artistic Freedom
Asvoria coming up soon!

 I’ll soon travel to Bulgaria to film some content in the Asvoria linked Hotel Satoshi Nakamoto, as well as guide the team on advances in our shiny updated metaverse space.
I’ll soon travel to Bulgaria to film some content in the Asvoria linked Hotel Satoshi Nakamoto, as well as guide the team on advances in our shiny updated metaverse space.
The art cars are also gearing up for their auction in Dubai in January, but more on that later.
See you Dec 5th 20.00 CET:
Link to join the metaverse
Link to join the X spaces.
Much to build,
VESA
Crypto Artist, Speaker, Consultant, Writer
All links to physical, NFTs, and more below





























✓ Share: